Transparent and efficient management of land records is vital for improved governance. As it directly contributes to boosting public confidence and it leads to socio-economic uplift of the society. With the rapid intervention of IT in every sector of life, the land administration in KP is also being transformed into digitized mode. Intervention of GIS technology has also been made in the ongoing settlement operations. GIS technology has the capabilities of capturing/collecting, storing, manipulating, analyzing, and displaying the geo-referenced data, which would bring transparency, efficiency and speed to the land transactions.
The traditional steps of Settlement have not been skipped in the GIS Based Settlement. In fact, the technological intervention has been made to quicken the process and to make it transparent. Thus, it will not only reduce time but will also ensure hassle free provision of services to the citizen. It also adds accuracy, which is so vital in Land Administration.
The detail process is discussed below and is shown in Figure 1.
The process of creating a rough Sketch of a revenue estate, or more precisely, the procedure for establishing the boundary of that revenue estate. GIS will assist this process by printing out high-definition satellite imagery on paper. With the assistance of the community and landowners, the Tehsildar/Patwari will be in charge of establishing the boundary line.
In settlement each and every parcel is measured. In traditional settlement plain table survey technique are applied. The entire process is laborious, time consuming and prone to error. With GIS intervention the measurement process is quickened and accurate. Both the products of measurement (field book and massive) are auto generated and multiple copies could be obtained.
Field Book preparation:
The production of the Field Book will be significantly simpler with GIS-based technologies. Using advanced surveying tools or fine resolution satellite imagery, each Khasra's dimensions will be measured. Patwari will note the Khatoni No. from the field, which will serve as the foundation for cross-checking the data.
Massavi preparation/Verification:
Massavi plotting by hand takes a very high level of expertise. These Massavis will be produced by GIS Associates. Before it is finalized, Massavis will be confirmed locally by concerned revenue officials. The scale for this Massavi will be the same as that for the manual one, or 1 inch = 40 Karam or 220 feet.
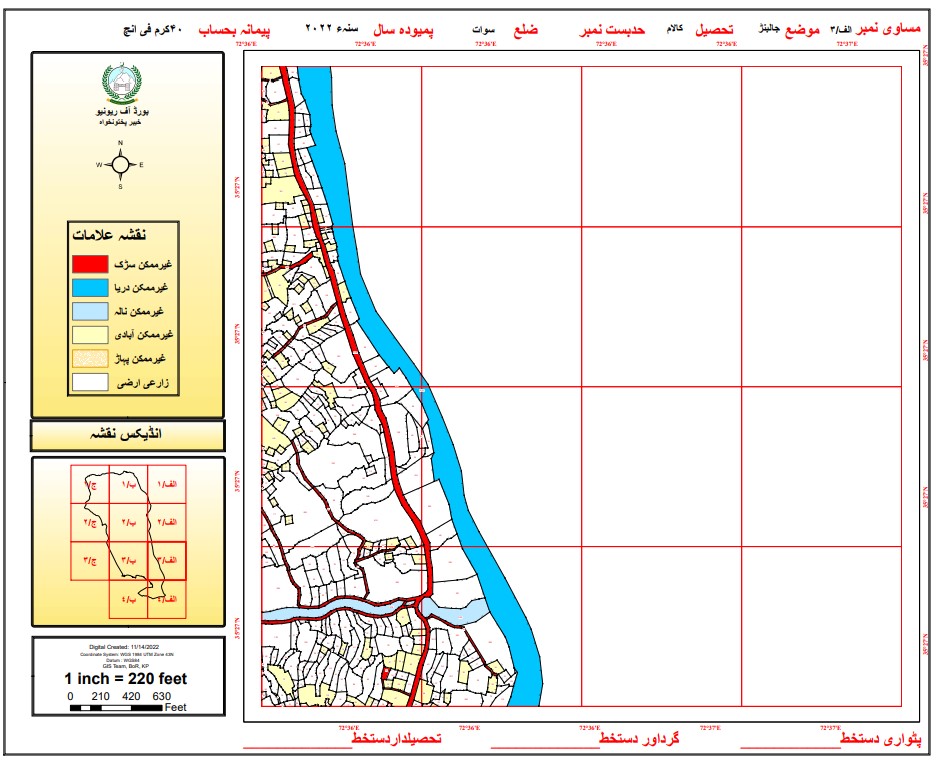
Figure 2. Digitized Massavi layout
After the completion of Mouza Massavi’s, the data is then validated through field verification
The Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is a relatively simple method of improving the positional accuracy of the receiver. Differential GPS consists of a GPS receiver, which needs to be set upon a precisely known location (benchmark). This GPS receiver is the base or reference station. The base station receiver calculates its position based on satellite signals and compares this positional information to the benchmark. The difference is applied to the GPS data recorded by the second GPS receiver (rover), and the accurate positional information is then recorded by the rover. The same technique will be used in this project. Each parcel will be measured through DGPS by the surveyors in the field. The rover data would be compared with the base station, and accurate measurements would be made. For this purpose, the densification of benchmarks has already been done by the Survey of Pakistan in the project area.
So, the Modern technology will be used for:
- Land title surveying
- Land parcel development and administration
- Survey database management
- GIS cadastral database management
- Automated electronic survey and database workflow tools for implementation
- Online publishing of Land records owners with integration of Geospatial data
Settlement Module has already been developed in LRMIS software by Deputy Director Database (PMU). The module has following functionalities:
Data Entry Module:
- Shajra Nasab data entry
- Khatoni data entry
- Field Book data entry
- Data Preparation/Generation Module
- Preparation / generation of Misl-e-Haqiat
- Reports of inconsistent Khatas/Khatonis
- Generation of Parcha Khatoni for Taqseem Parcha Khatoni process
Mr. Aftab Ahmad
Deputy Director GIS
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system that creates, manages, analyzes, and maps all types of data. GIS connects data to a map, integrating location data (where things are) with all types of descriptive information (what things are like there). This provides a foundation for mapping and analysis that is used in science and almost every industry. GIS helps users understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context. The benefits include improved communication and efficiency as well as better management and decision making.