|
Factor
|
Traditional Method
|
Technology Based (GIS based)
|
|
Time
|
It takes years to complete
|
It can reduce time from months to days
|
|
Measurements
|
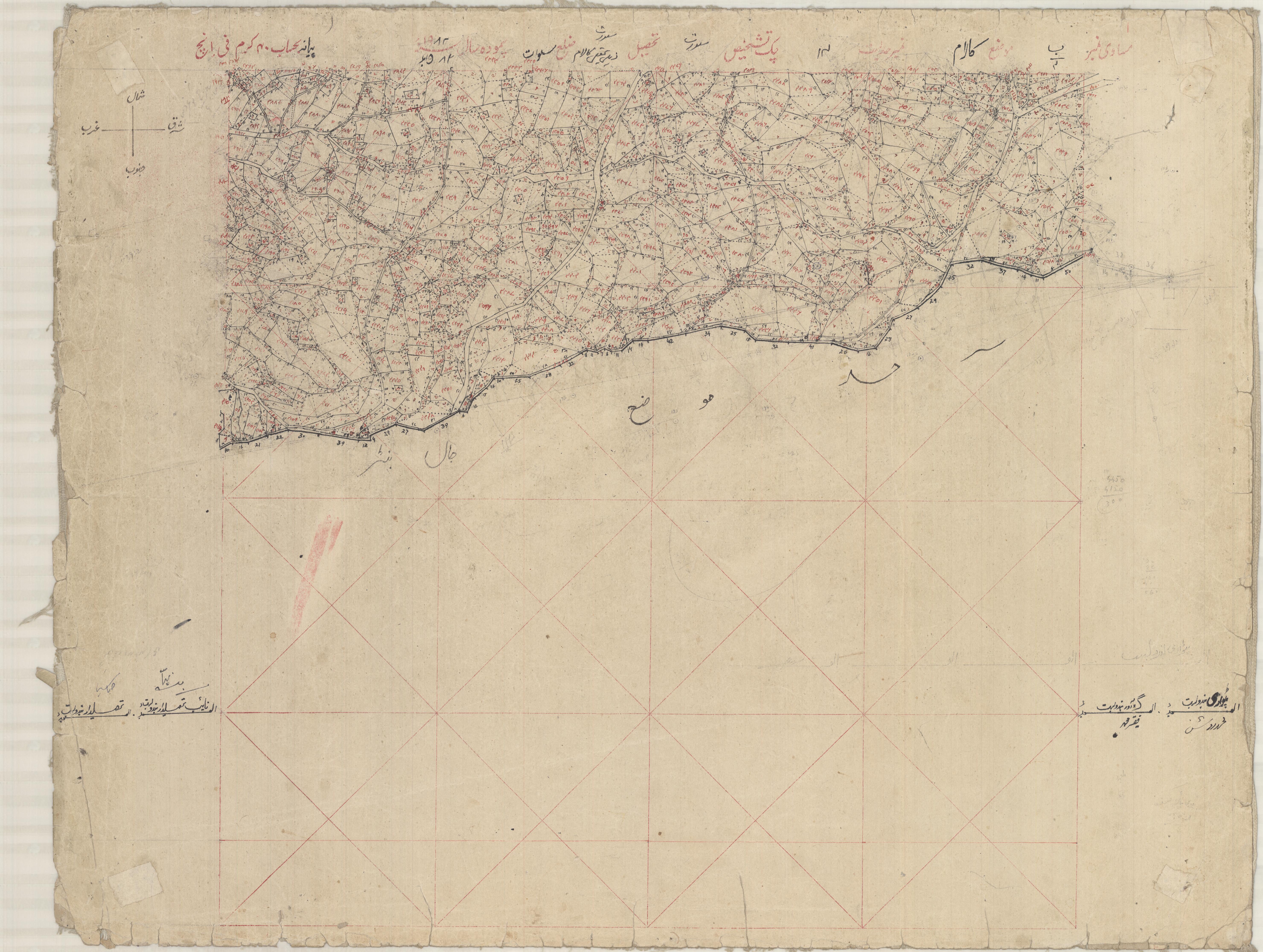
Each Khasra (parcel) is measured using manual methods like chain survey & plain table.
|
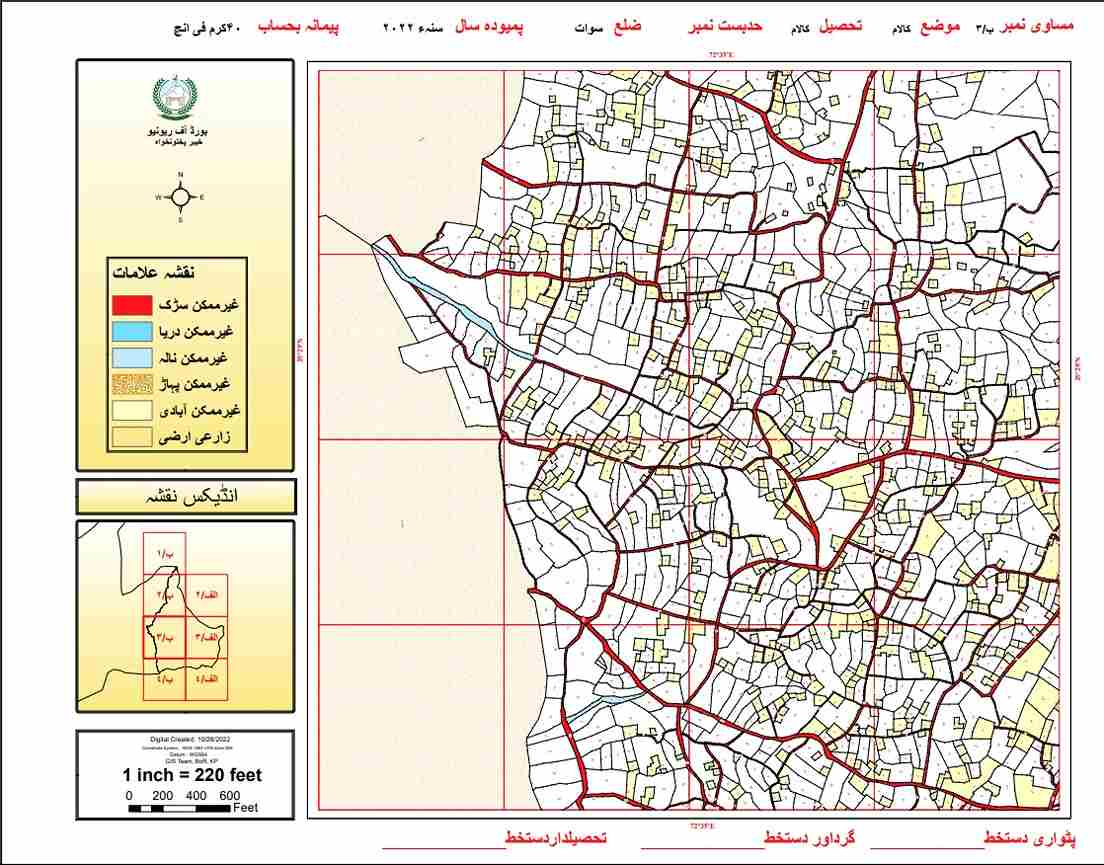
Measurements are done through high resolution satellite imagery,
UAVs or advanced survey equipment
|
|
Accuracy
|
Manual methods has its inherent inaccuracy even if
the measurements are done by experts. Several feet(5.5 to 11 ft) inaccuracy is
considered condonable
|
Digital surveys can provide accuracy up to centimeters and hence the
area calculations are accurate.
|
| Irregular Khasra boundaries
|
In case of irregular Khasra boundary, revenue staff do a lot of trigonometric calculations which may lead to inaccuracies and hence incorrect area calculation.
|
No extra calculations required |
| Development of Massavi maps
|
Maps are drawn by hand using plane tabling technique which requires a high level
expertise in this field. Chances of errors are very high in this process.
In case of any error, it takes a lot of time to correct.
|
Maps are produced digitally and chances of errors are minimal. In case of any
error it can be corrected in a very short time.
|
| Duplicate of Massavi maps
|
One of the requirement of settlement is to produce duplicate Massavi. It is done
using tracing paper and is time consuming activity. Chances of error are very high
as well.
|
Once a digital Massavi map is developed,
unlimited copies can be produced with a click of button |
| Geographic reference of Massavi map
|
Massavi maps lack geographic reference and usually the references used cannot be
identified on ground. There is no coordinate system defined for Massavi map.
|
Maps are geographically referenced and Khasra can be located easily |
| Post Settlement Demarcations/Acquisitions
|
Khasra demarcation is usually started from permanent points
(Sehada) which do not exist on ground. At times accurate demarcation becomes
impossible |
Each Khasra will be geo referenced. Hence, future demarcation should not be
an issue.
|
| Usability of Maps
|
Massavi maps cannot be used to produce different
scales of map like Mouza, Tehsil, District. |
Different scales of maps can be produced
|
| Security and backup
|
A very proper mechanism is used to preserve original Massavi maps and it
is prone to wear and tear, it can be lost/stolen, can be destroyed in floods,
earthquakes or in case of fire.
|
It is produced in digital format so different backups at different
places ensure its security and it can be printed any time.
|
| Cost
|
Most of the cost is of staff salaries and operational costs.
|
Initial cost of equipment and software may be higher but in the long
run it is much cheaper than the traditional method.
|
| Computerization
|
Once the settlement process is complete, a huge amount will be required
to computerize it.
|
Record will be computerized from the start and it will save this cost |
| Transparency
|
Human based system. Human error in share calculations,
updating transactions in Jamabandi are possible.
|
Technology based system. Share calculation and updating
transactions in Jamabandi are automated.
|
| Record Accessibility
|
No centralized facility for viewing of record.
Record maintained at one or two points (Patwar Khana and District Record Room).
|
CLRMIS makes it possible to view and get a copy of record from multiple points.
|
| Tax Collection
|
Not linked with FBR. Heavily reliant on manually
calculated data of Mouza or, at best, of District |
Could be linked with
FBR/Nadra. System generated data can be
extracted even for the entire Province |
| National/Global Requirements
|
Not synchronized with the modern digital world.
Seems obsolete even as per national standard of transformation to the digital system |
In line with global land Record Management Systems.
Can be linked with national databases such as Nadra, FBR, other BORs and Banks etc |
| Traditional vs GIS Based Massavis |
|
|